GLIA-CTN Enrollment and Natural History Data
The Global Leukodystrophy Initiative Clinical Trials Network (GLIA-CTN) is a consortium of scientists, industry stakeholders, and patient advocacy leaders working together to promote advances in the diagnosis and treatment of leukodystrophies. The Global Leukodystrophy Initiative Clinical Trials Network (GLIA-CTN) is part of the Rare Diseases Clinical Research Network (RDCRN) which is funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and led by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) through its Division of Rare Diseases Research Innovation (DRDRI). GLIA-CTN is funded under grant number U54NS115052 as a collaboration between NCATS and the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS).
US Enrollment by Region
Note that enrollments are rounded up to the nearest increment of 5 for privacy reasons.
Cumulative Enrollment
Enrollment by Sex and Race/Ethnicity
Note that enrollments are rounded up to the nearest increment of 5 for privacy reasons.
Copyright 2026 by The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
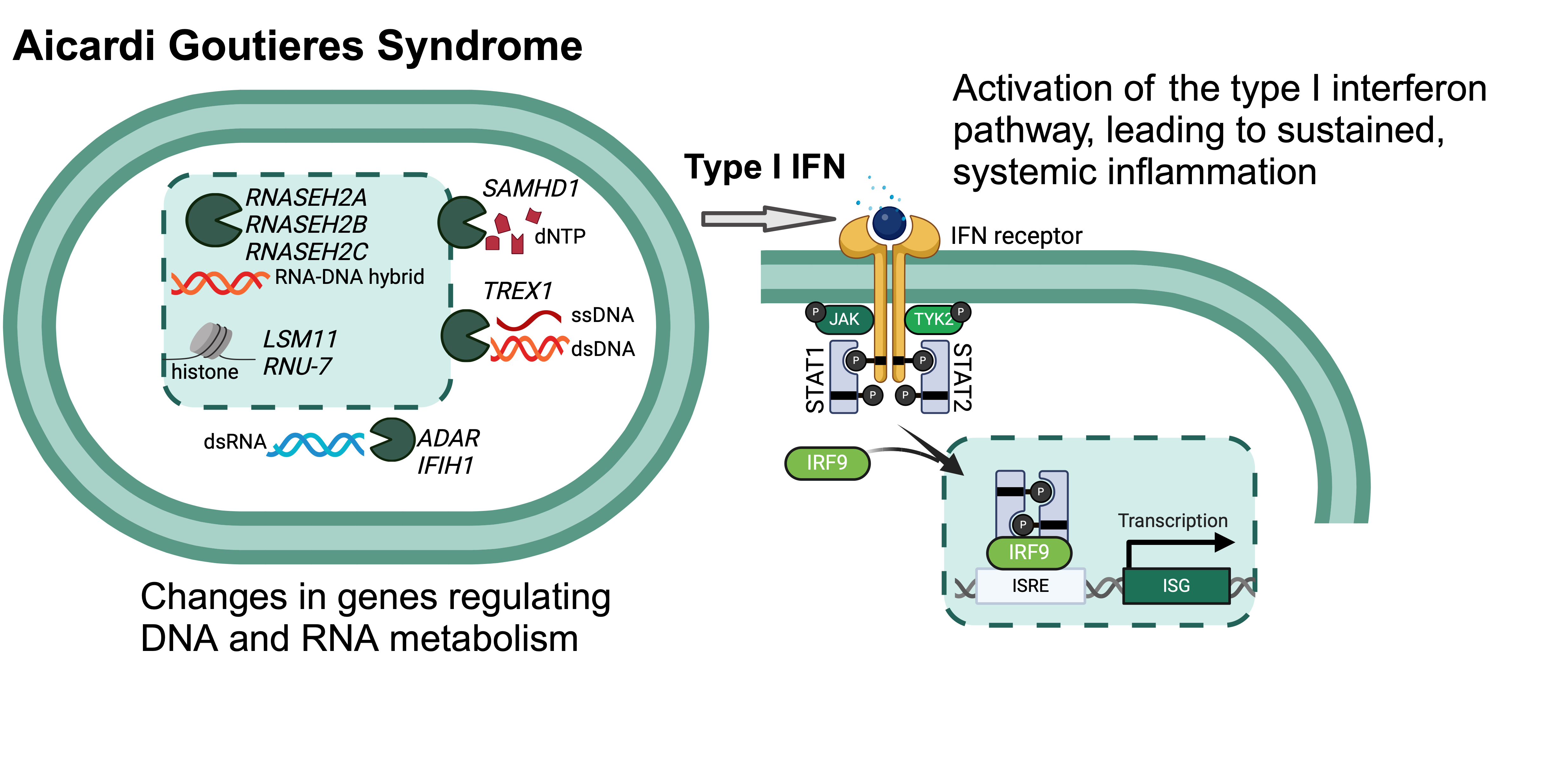
Terms of UseAicardi Goutieres Syndrome (AGS) is an inherited type I interferonopathy caused by disruption of DNA and RNA metabolism. While it was originally described as a mimic of severe congenital infection, AGS is now recognized to cause a broad range of disease. AGS is associated with multi-systemic disease burden, including pulmonary hypertension, chilblains (vascular disease of the skin), and glaucoma.
Biological mechanism of AGS
Select GLIA-CTN AGS projects
Variant curation. The GLIA-CTN has partnered with ClinGen to establish Gene and Variant Curation Expert to provide comprehensive variant curation, including the most clinically actionable disease-causing variants. This project will support the disease-gene association in the leukodystrophies and clarify the pathogenicity of variants in key high frequency genes.
AGS biomarker study. We are exploring how to best diagnose AGS by developing novel panels of biomarkers.
AGS natural history study. We are using real world data (existing medical records) to map the full history of patients affected by AGS. We are focusing especially on the early period prior to diagnosis.
AGS prospective natural history study. We are measuring skills related to movement and cognition in AGS using application of traditional outcome measures.
AGS Natural History Encounters per Patient
AGS Natural History Onset
Confirmed Disease Causing Variants
Outcome Assessments
Time to Feeding Tube Placement
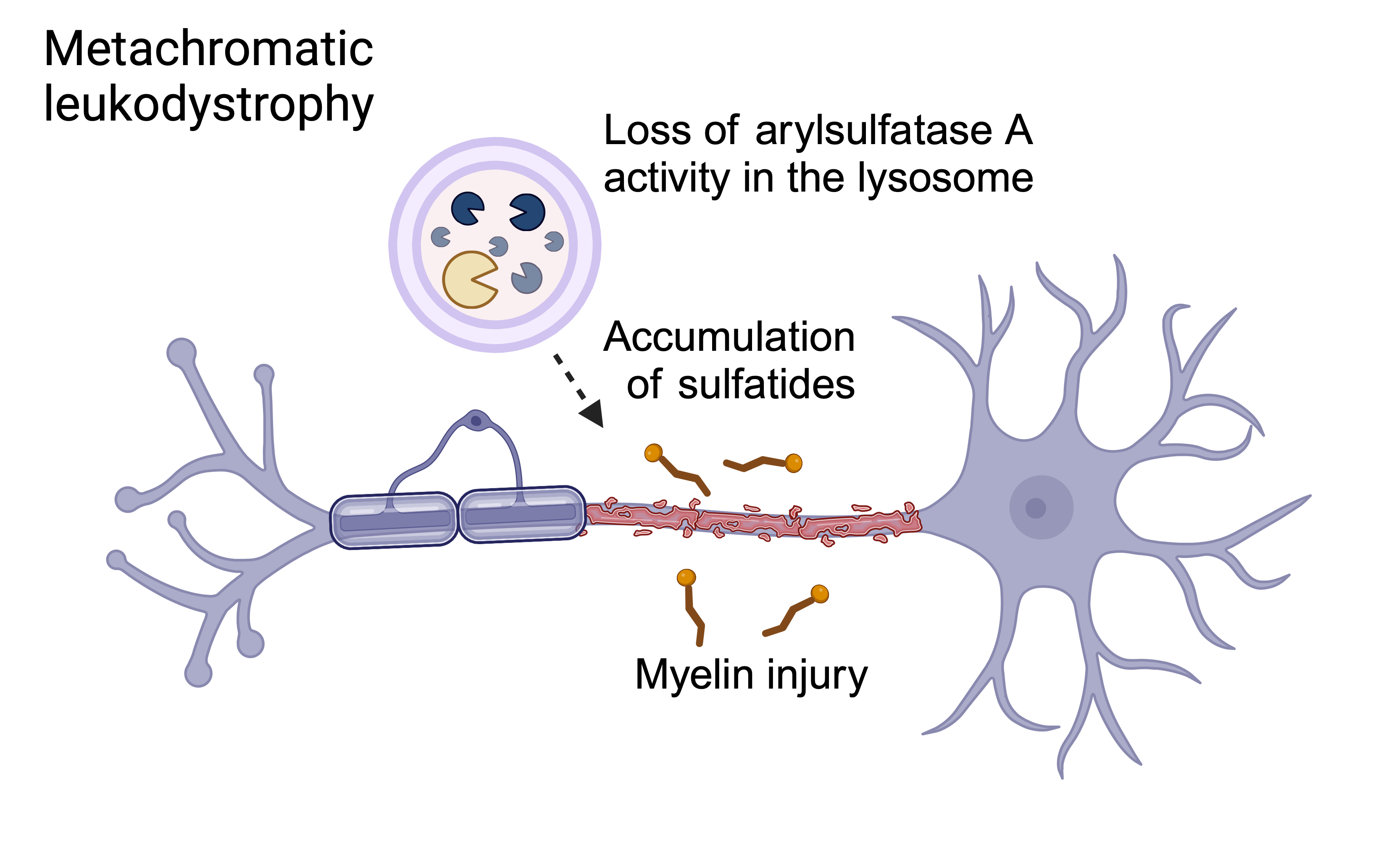
Metachromatic leukodystrophy (MLD) is a progressive neurodegenerative lysosomal disorder that affects both the central and peripheral nervous systems. It is the result of biallelic variants in the ARSA gene, which encodes the lysomal enzyme arylsulfatase A. This results in accumulation of sulfatides, which can be found in elevated levels in the blood, urine, and cerebrospinal fluid. There are 4 subtypes of MLD, which are defined by age at onset: late infantile (LI), early juvenile (EJ), late juvenile (LJ), and adult MLD.
Biological mechanism of MLD
Select GLIA-CTN MLD projects
Variant curation. The GLIA-CTN has partnered with ClinGen to establish Gene and Variant Curation Expert to provide comprehensive variant curation, including the most clinically actionable disease-causing variants. This project will support the disease-gene association in the leukodystrophies and clarify the pathogenicity of variants in key high frequency genes.
Expansion of the validation of GMFC-MLD. The Gross Motor Function Classification-MLD (GMFC-MLD) is a disease specific tool that enables the mapping of neurological function in prospective and retrospective applications. This assessment is scored in children above the age of 18 months according to a seven-item categorical scale from normal ambulation (M0) to no mobility or head control (M6). As part of this project, we will explore its use across the MLD subtypes and define its proportionality to other outcome measures.
MLD natural history study. We are using real world data (existing medical records) to map the full history of patients affected by MLD. We are focusing especially on the early period prior to diagnosis.
MLD prospective natural history study. We are measuring skills related to movement and cognition in MLD using application of traditional outcome measures. We are focusing on all age groups, including the adult patients.
MLD Natural History Encounters per Patient
MLD Natural History Onset
Confirmed Disease Causing Variants
Outcome Assessments
Time to Feeding Tube Placement
Time to Loss of Ambulation
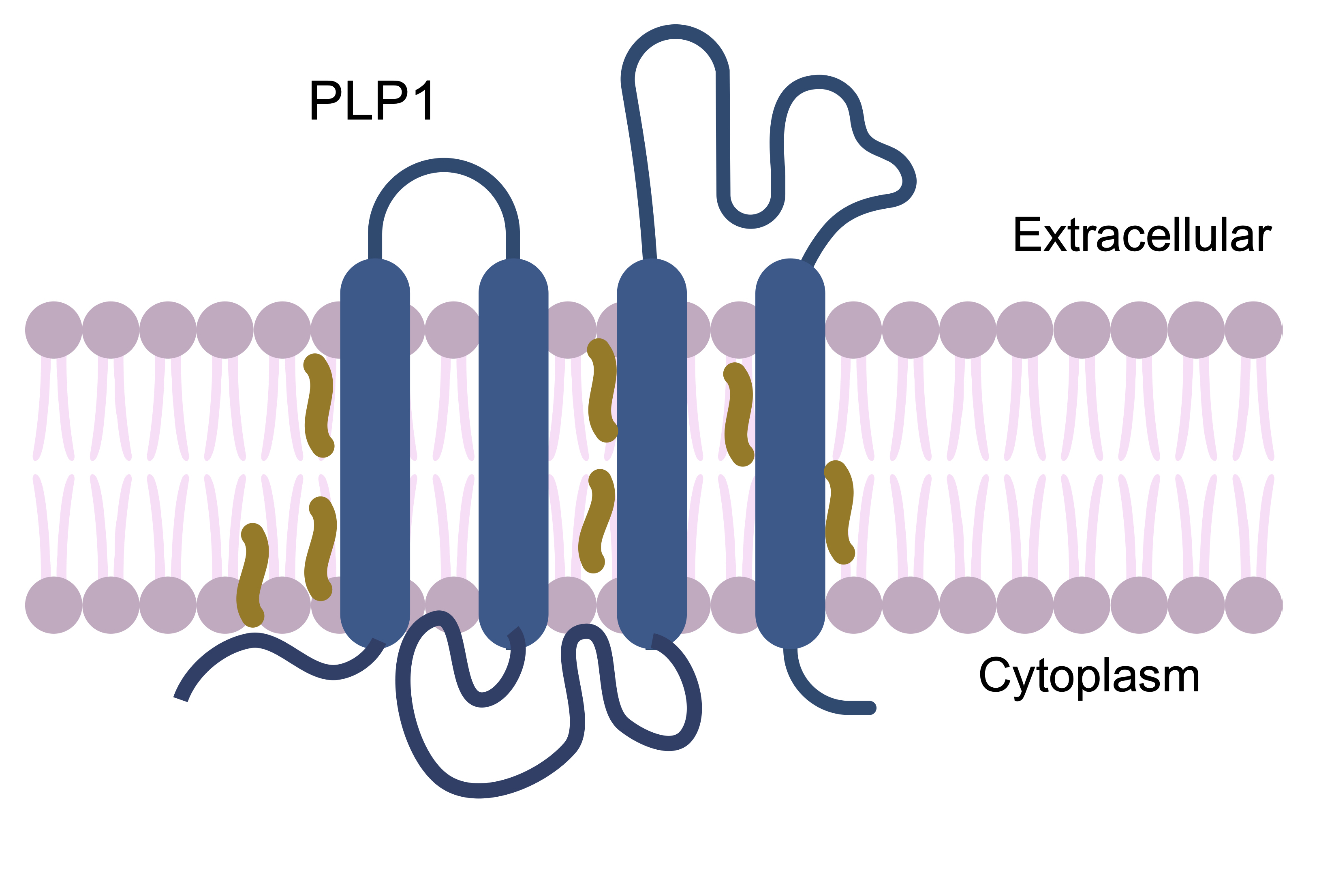
Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease (PMD) is an X-linked disorder caused by pathogenic variants in a myelin protein encoded by PLP1. It most commonly presents in infancy with nystagmus, hypotonia, and cognitive impairment. Changes in the same gene also result in an attenuated phenotype, spastic paraplegia 2 (SPG2).
Biological mechanism of PMD
Select GLIA-CTN PMD projects
Variant curation. The GLIA-CTN has partnered with ClinGen to establish Gene and Variant Curation Expert to provide comprehensive variant curation, including the most clinically actionable disease-causing variants. This project will support the disease-gene association in the leukodystrophies and clarify the pathogenicity of variants in key high frequency genes.
PMD natural history study. We are using real world data (existing medical records) to map the full history of patients affected by PMD. We are focusing especially on the early period prior to diagnosis.
PMD prospective natural history study. We are measuring skills related to movement and cognition in PMD using application of traditional outcome measures.
PMD Natural History Encounters per Patient
PMD Natural History Onset
Outcome Assessments
Time to Feeding Tube Placement
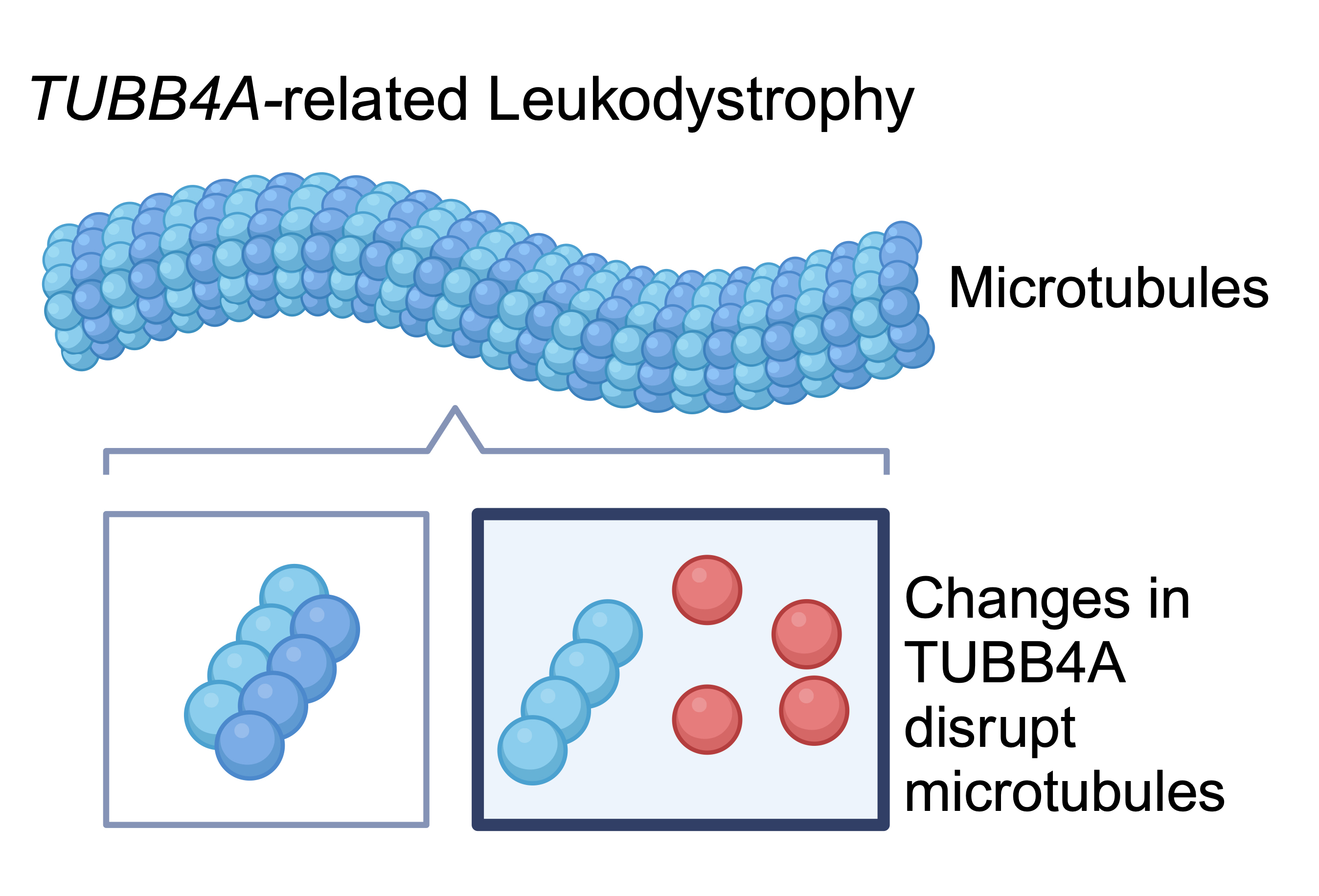
TUBB4A-related leukodystrophy represents a spectrum of disease defined largely by radiographic features: hypomyelination with atrophy of the basal ganglia and cerebellum (H-ABC) to isolated hypomyelination. It is associated with an adult whispering dysphonia (DYT4) phenotype as well.
Biological mechanism of TUBB4A
Select GLIA-CTN TUBB4A projects
Variant curation. The GLIA-CTN has partnered with ClinGen to establish Gene and Variant Curation Expert to provide comprehensive variant curation, including the most clinically actionable disease-causing variants. This project will support the disease-gene association in the leukodystrophies and clarify the pathogenicity of variants in key high frequency genes.
TUBB4A natural history study. We are using real world data (existing medical records) to map the full history of patients affected by TUBB4A. We are focusing especially on the early period prior to diagnosis.
TUBB4A prospective natural history study. We are measuring skills related to movement and cognition in TUBB4A using application of traditional outcome measures.